N435
Optocoupler (photo-transistor type)
The 4N35 is an optocoupler that consists of a gallium arsenide infrared LED and a silicon NPN phototransistor. When the input signal is applied to the LED in the input terminal, the LED lights up. After receiving the light signal, the light receiver then converts it into electrical signal and outputs the signal directly or after amplifying it into a standard digital level. Thus, the transition and transmission of electricity-light-electricity is completed. Since light is the media of the transmission, meaning the input terminal and the output one are isolated electrically, this process is also be known as electrical isolation.
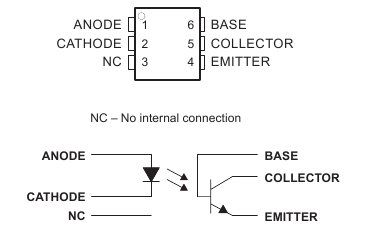
Current from the source signal passes through the input LED which emits an infra-red light whose intensity is proportional to the electrical signal.
Pin 1 and 2 are connected
to an infrared LED. When the LED is electrified, it'll emit infrared rays. To protect the LED from burning, usually a resistor (about 1K) is connected to pin 1. Then the NPN phototransistor is power on when receiving the rays. This can be done to control the load connected to the phototransistor. Even when the load short circuit occurs, it won't affect the control board, thus realizing good electrical isolation.
Optocoupler functions as a galvanic isolation component. That is it maintains the connection between two devices or component without any direct conduction.
#2, IC.01.2
Datasheet
Arduino 17 project